How to Improve Site Performance
In this article, we're going to explain how to optimize your website performance in order to provide your visitors the best experience possible.
To better equip you with specific performance enhancement techniques, we have put together this article and will use it as a foundation to build upon. As a company we are committed to performance and keeping things as efficient as possible. While there are only so many things a theme can do to optimize for performance, the vast majority of performance improvements will be seen by properly setting up and configuring some of the options discussed on this page. Please keep in mind that this list is for information purposes and is not a guarantee. Even when following these steps, performance issues can persist due to external forces outside of your immediate control (limited memory allocation from your hosting company, over sold server, user on your server utilizing more than their share of resources, etc). While we are unable to provide support for 3rd party plugins or scripts not integrated into the theme, we do hope this helps provide a good foundation for user side optimizations focused on performance.
Important Note Before Getting Started: While you are building and developing your site, it's advised to turn off caching. This is especially important if you are working with our support team. It's possible to implement a change, and not have it take place because a cached version of the page or various resources are loading instead of the latest version.
Why Website Performance is Important
When it comes to running a successful website one of the most important metrics is website speed. The fast load time of a page will help to increase search engine rankings and provide your visitors with a pleasant web experience.
Caching
The most important and often oversight part of optimizing your site is caching. Caching is a broad term and most people think with simply enabling a caching option is a done deal. Unfortunately, it’s more complex than this and that’s why we created this knowledge base article here to give you a little crash course about all of the little things to watch out when optimizing your site.
A database driven content management system like WordPress always generates and reads data out of the database, so every information that is dynamic gets pulled from a database which creates a requests. As you might know this can add up easily leading to a lot of requests and therefore the idea about caching is minimizing those requests after the first visit.
On the first visit your browser loads all the data and doing all the database requests, now if you do not have any caching in place this will be repeated every time you click another page link or reload the page. To prevent this from happening most of the sites use caching. Caching is recognizing which parts of your site are not changing frequently and cache them so they do not have to get loaded another time when switching page or reloading. This decreases server load and increases site speed for the user since the browser has to handle less requests.
W3 Total Cache
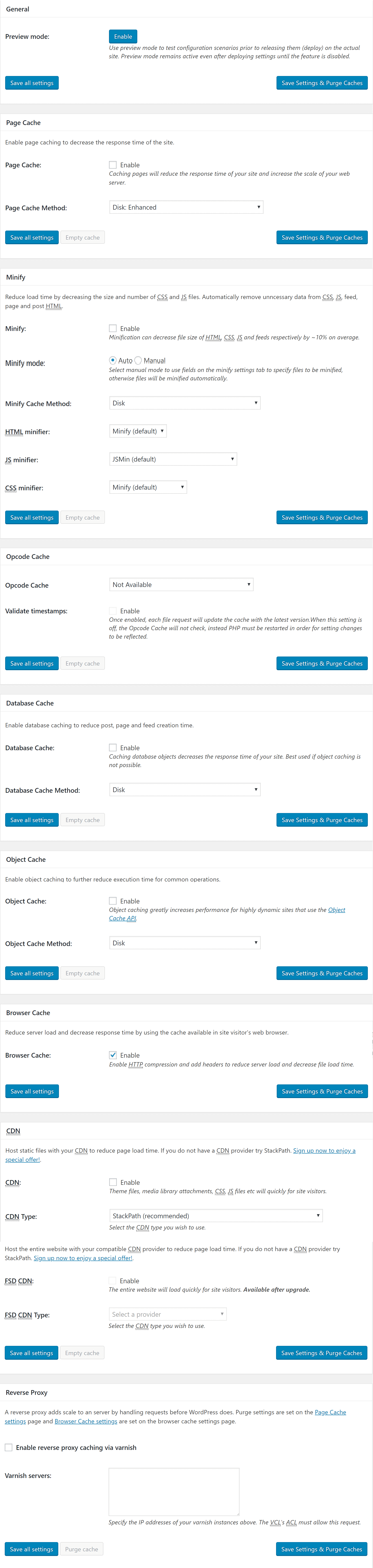
The most basic and very easy approach to enable caching is getting a plugin called W3 Total Cache.
After activating the plugin it comes with a default set of settings which you can alter but be aware that if you do not know what you are doing this could lead to site loading problems so we recommend sticking to our tutorial on what to change and do not touch the rest.
The default settings of W3TC should be fine for most users but if you are a person that really wants to get into this matter and optimize every inch out of your website then you can do some tweaks like:
Page Cache
Set the Page Cache option to enabled and as page cache method pick disk enhanced or if you are running a VPS or dedicated server then install memcached and use memcached as caching method. Memcached is a distributed memory object caching system which is recommended if you are running bigger sites since it reduces the server load and performs better with a lot of traffic on your site.
Minify
All of the X assets come pre-minified, so this is only needed if you're using plugins that include their own scripts and styles. If that's the case, enable Minify and set the mode to auto. Use the default settings for the rest. Keep in mind that if you're using a large number of plugins, script minification and concatenation can cause plugin conflicts. If you run into any issues, you can disable this feature.
Database Cache
Make sure to enable this option as well and as cache method use Disk. (Leave this off if you're going to configure a CDN later)
Object Cache
Also enable Object Cache and use the Disk method.
Browser Cache
Enable this too.
Network Performance & Security
We will cover this in another topic after this one so leave it empty/deactivated for now.
For the rest of the settings just keep them as they are out of the box.
Gzip Compression
The idea of Gzip is to compress and decrease the size of the content that the browser has to load. This increases the speed for the user and the bandwidth usage of the server so it’s a win - win situation for both sides.
Plugins like W3 Total Cache have the option to do Gzip compression for your site but most people prefer to use the native way so they are independent or if you do not want to use the W3TC plugin then this is something you can do on its own to increase performance.
Open up the .htaccess file in your root WordPress directory and add following:
<IfModule mod_deflate.c>
# Force compression for mangled headers.
<IfModule mod_setenvif.c>
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
SetEnvIfNoCase ^(Accept-EncodXng|X-cept-Encoding|X{15}|~{15}|-{15})$ ^((gzip|deflate)\s*,?\s*)+|[X~-]{4,13}$ HAVE_Accept-Encoding
RequestHeader append Accept-Encoding "gzip,deflate" env=HAVE_Accept-Encoding
</IfModule>
</IfModule>
# Compress all output labeled with one of the following MIME-types
# (for Apache versions below 2.3.7, you don't need to enable `mod_filter`
# and can remove the `<IfModule mod_filter.c>` and `</IfModule>` lines
# as `AddOutputFilterByType` is still in the core directives).
<IfModule mod_filter.c>
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/atom+xml \
application/javascript \
application/json \
application/ld+json \
application/rss+xml \
application/vnd.ms-fontobject \
application/x-font-ttf \
application/x-web-app-manifest+json \
application/xhtml+xml \
application/xml \
font/opentype \
image/svg+xml \
image/x-icon \
text/css \
text/html \
text/plain \
text/x-component \
text/xml
</IfModule>
</IfModule>Content Delivery Network
Content Delivery Networks, short CDNs can be a huge speed boost and also reduce server load by a lot. A CDN stores data from your site for example images, javascript, css so you are basically outsourcing your files to another server. Why would you do that?
Modern browsers limit the number of concurrent connections this means if you have 10 files to load on your server it only can load 2 at a time. So it takes some time till 10 are loaded. If you have some of your content on a CDN it can load for example 4 or 6 or even more files at once which increases the page loading speed by a lot. Also the images, JS or CSS which you store on CDNs is spread around servers around the world so it will always pick the closest location from your user and delivery the content. It also decreases bandwidth and disk space as well as server load from your main server so you are saving money by being able to use a lower specced server or web space since the server has to handle less things.
MaxCDN is one of the most popular Content Delivery Networks and it can be integrated with the W3 Total Cache plugin which is great since then it’s very easy to implement and for people who are not so tech savvy this is a huge plus. You also can integrate it manually MaxCDN provides a lot of tutorials on how to do that so that won’t be a problem.
Cloudflare
Content Delivery Networks & DNS provider like Cloudflare can be one of the biggest speed boosts overall if you have a very broad international audience. So what is it doing? Imagine having several hundreds of servers around the world and on each server there is a copy of your website. Now if a user visits your site a smart script finds out the location of that person and routes him to the closest server from his location and uses that server to display your site. This means if a person from Dallas is visiting your site it will be routed to a server in Dallas. If a person from Paris is visiting your site it will be routed to a server in Paris. This decreases response time and overall loading time tremendously since the delay time is a lot lower than usually. Another benefit is if one of those servers goes down you have many other servers still running so your site will always be available even if some of the servers would have outages this maximizes your uptime. Best of all it’s free!
Image Compression
Image Compression is a crucial thing to do but most people forget it and then are wondering why their site loading speed is very slow. Images are one of the biggest part of your website. An image heavy site can still be quick if you watch out for some things which we will cover in a second.
First of all, always try to use JPEG or GIFs rather than PNGs since they are smaller in size. A lot of people upload their big images and WordPress will crop them in all the different thumbnail sizes and you will insert the image with the proper thumbnail size in the post and then people think it’s all set.
But the most important thing to do is compressing your images otherwise you will have big images and a slow loading time. There are different ways on how to compress images. Below are a couple of services and WordPress plugins you can use to optimize your images for decreased loading times.
- WP Smush Pro (WPMU DEV). Smush Pro is a cloud based image optimizing plugin, that works on a API based system, that allows you with a few clicks to send your images for optimizing and also includes lossless compression with it's Super Smush option.
- Kraken.io Kraken is another cloud based image optimization service, the main difference being, they not only have a WordPress plugin you can use, but you can also optimize images directly on their website, rather than using the plugin.
- Ewww Image Optimizer Ewww Image optimizer is another cloud based image optimization plugin, that also allows you to optimize and compress images to decrease load times.
If you are creating images in Photoshop a common thing that people do wrong is save the images without using the option “Save for Web & Devices”. This is very crucial since you can set there the compression and quality rate and other things which will lead to a smaller image size. Other image editing programs can do the same so always look in the documentation for image compression.
Plugin Management
Something that most users forget is that plugin management is key. Keeping the plugins up to date is not enough, you really should see each plugin as performance decrease which adds bloat to your site so the first thing to do is to ask yourself “do I really need all of these plugins”. Keeping the plugin amount to a minimum is key for a quick and well optimized site. Anytime you run multiple plugins from multiple companies you run the risk of poor performance issues due to any number of things including different development approaches (theme vs plugin developer), user configuration error, server restrictions, etc.. The reality is that unless the theme and plugin were developed by the same company, you run the risk of numerous compatibility issues including performance issues.
Choosing the Correct Hosting Service Plan
Webspace is not Webspace. There are huge quality differences and also finding the right size of webspace for your site can be a daunting task. There are just a few general rules of thumb which we can give you but most of the time it's up to the individual needs which webspace you should get.
The first question you will face is do you need a shared webspace, a VPS or a dedicated server. For most people a shared server is enough if you have under 1000 visitors a day you should be more than fine with most of the webspaces out there, make sure that it has enough bandwidth and uses the latest software preferable instead of apache something like Litespeed which can increase the performance of your site and server. When it comes to VPS it’s a bit more challenging since you need to decide how much disk space and how much ram you will need. The good thing about VPS is that upgrading is very quick and easy since all the limits are virtual emulated so with a reboot from the hosting company they can change all the values so we would recommend going with the lowest possible and see how it performs to save money.
Dedicated servers are a whole new level. You have a whole server for yourself and a lot of things to worry about. First of all it’s important to decide if you go with a managed or unmanaged server. If you choose the cheaper method which is unmanaged you should have some experience in server administration since updates from software and keeping the server secure is crucial and there is no support to ask if there are problems. But even owning a managed server does not mean that you should not update the server and have an overlooking eye on it. Managed server just means if you have troubles or if there are really crucial server updates they will be handled by the hosting company but for the rest it’s still your call.
When it comes to site performance the webspace is crucial. Things like having a SSD server, running Litespeed and having enough resources like ram are key to provide a smooth experience for your users.
Summary
You are now familiar with basic steps to optimize your website and provide your visitors a pleasant experience.
See something inaccurate? Let us know